SOC 2 Requirements
SOC 2 is an auditing procedure for ensuring service providers have proper data and privacy protections in place for sensitivity data. Organizations working to achieve SOC 2 certification must implement a series of controls and go through an audit with an external auditor.
Auditors assess organization compliance with one or more of the AICPA Trust Services Criteria (TSC). Teams must have all applicable controls in place and be able to provide evidence of control effectiveness in order to achieve SOC 2 certification and receive a SOC 2 report.
Download full SOC 2 Controls List XLS
SOC 2 Trust Services Criteria (TSC)
In order to achieve SOC 2 certification and meet the latest SOC 2 report framework standards, teams must implement the latest 2017 Trust Services Criteria (TSC).
The Trust Services Criteria (previously Trust Services Principles) are a set of criteria and related controls that organizations must implement across your organization and IT infrastructure. The five categories of control criteria are:
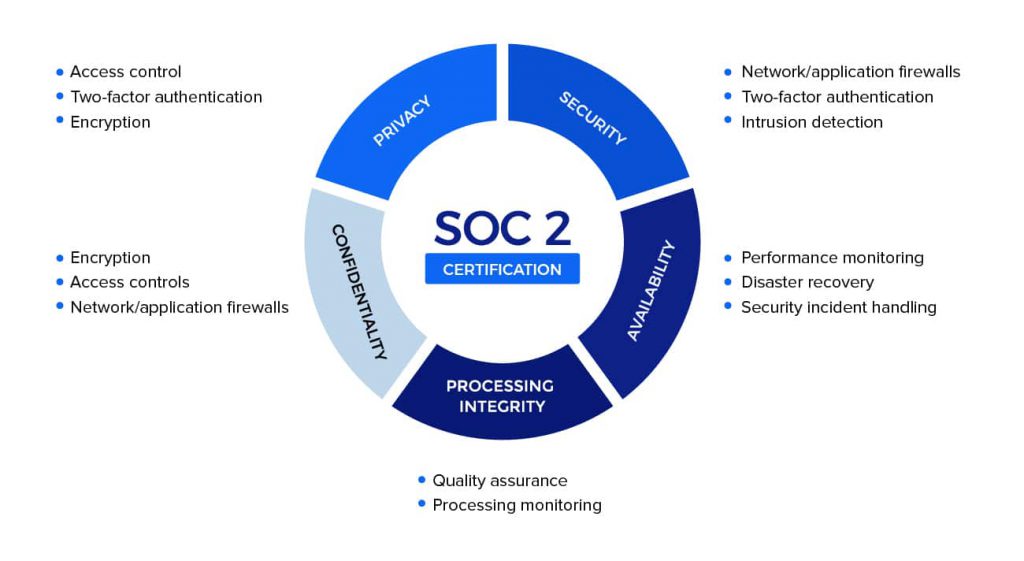
Security
A business’s data and computing systems are fully protected against any unauthorized access, unauthorized and inappropriate disclosure of information, and any possible damage to systems that might compromise the processing integrity, availability, confidentiality or privacy of data or systems that may affect the entity’s ability to meet its objectives.
Security criteria refers to your organization’s protection of:
- Information during its collection or creation, use, processing, transmission, and storage.
- Systems that use electronic information to process, transmit or transfer, and store information to enable your organization to meet its objectives. Controls over security prevent or detect the breakdown and circumvention of segregation of duties, system failure, incorrect processing, theft or other unauthorized removal of information or system resources, misuse of software, and improper access to or use of, alteration, destruction, or disclosure of information.
Availability
All information and computing systems are always ready and available for operation and use to meet the entity’s objectives.
Availability refers to the accessibility of information used by your organization’s systems as well as the products or services provided to its customers.
- The availability objective does not, in itself, set a minimum acceptable performance level.
- It does address whether systems include controls to support accessibility for operation, monitoring, and maintenance.
- It does not address system functionality (the specific functions a system performs) or usability (the ability of users to apply system functions to the performance of specific tasks or problems).
Processing Integrity
All system processing is complete, accurate, valid, timely and authorized to ensure that the entity meets its objectives.
Processing integrity refers to your organization’s controls and procedures around:
- Verifying the completeness, validity, accuracy, timeliness, and authorization of system processing.
- Determining whether systems achieve the aim or purpose for which they exist and whether they perform their intended functions in an unimpaired manner, free from error, delay, omission, and unauthorized or inadvertent manipulation.
- Because of the number of systems used by an entity, processing integrity is usually only addressed at the system or functional level of an entity.
Confidentiality
Any information designated as confidential remains secure to meet the entity’s objectives.
Confidentiality refers to your organization’s controls and procedures including:
- Your organization’s ability to protect information designated as confidential from its collection/creation through its final disposition and removal
- Confidentiality requirements may be contained in laws or regulations or in contracts or agreements that contain commitments made to customers or others.
- Confidentiality differs from the privacy criteria, in that privacy applies only to personal information, whereas confidentiality applies to various types of sensitive information.
Privacy
All personal information collected, used, retained, stored, disclosed or disposed of must meet the entity’s objectives.
Privacy criteria examines your organization’s controls and procedures around:
- Notification and communication of objectives: Notifications to data subjects/users about objectives related to privacy.
- Choice and consent: Communication choices available regarding the collection, use, retention, disclosure, and disposal of personal information to data subjects.
- Collection: Collection of personal information to meet its objectives related to privacy.
- Use, retention, and disposal: Limits around the use, retention, and disposal of personal information to meet its objectives related to privacy.
- Access: Data subject access provided to their personal information for review and correction (including updates) to meet its objectives related to privacy.
- Disclosure and notification: How your organization discloses personal information, with the consent of the data subjects, to meet its objectives related to privacy. Notification of breaches and
incidents is provided to affected data subjects, regulators, and others to meet its objectives related to privacy. - Quality: How your organization collects and maintains accurate, up-to-date, complete, and relevant personal information to meet its objectives related to privacy.
- Monitoring and enforcement: How your organization monitors compliance to meet its objectives related to privacy, including procedures to address privacy-related inquiries, complaints, and disputes.
Organizations may be evaluated across one or more TSC categories during a SOC 2 audit. It is up to your team to prepare for a SOC 2 audit and have an established security program in place in order to streamline assessment and achieve certification. Once a SOC 2 assessor has validated your team’s security controls, they will write a SOC 2 report for your organization.
Alignment with COSO Framework
The latest 2017 TSC standards for SOC 2 reports integrate the 2013 COSO framework. COSO provides a generally accepted framework for internal controls within the organization. SOC 2 integrates the COSO framework including the five components of internal controls:
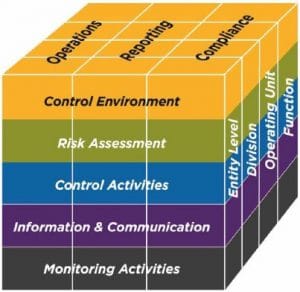
Control Environment
- Exercise integrity and ethical values.
- Make a commitment to competence.
- Use the board of directors and audit committee.
- Facilitate management’s philosophy and operating style.
- Create organizational structure.
- Issue assignment of authority and responsibility.
- Utilize human resources policies and procedures.
Risk Assessment
- Create company-wide objectives.
- Incorporate process-level objectives.
- Perform risk identification and analysis.
- Manage change.
Control Activities
- Follow policies and procedures.
- Improve security (application and network).
- Conduct application change management.
- Plan business continuity/backups.
- Perform outsourcing.
Information and Communication
- Measure quality of information.
- Measure effectiveness of communication.
Monitoring
- Perform ongoing monitoring.
- Conduct separate evaluations.
- Report deficiencies.
These components have been integrated into the latest SOC 2 Trust Services Criteria and provide a foundation for sound internal controls within the organization.
SOC 2 Controls List
SOC 2 criteria and controls cover a wide number of security best practices across IT infrastructure and your organization including risk management, physical and logical access controls, and system access. Teams should establish a security program and consider working with a team like Dash to perform readiness assessment and prepare for a SOC 2 audit.
The following categories of criteria are used to assess compliance with the SOC 2 Report Framework:
(CC1) Control Environment – These controls address with how the organization sets security roles, manages oversight and deals with security as related to employees, hiring, and overall management.
(CC2) Communication and Information – These controls address how teams communicate IT and security requirements, responsibilities and overall objectives across the organization.
(CC3) Risk Assessment – These controls address how organizations manage risk analysis and identify, address and accept risk across the organization.
(CC4) Monitoring Activities – These controls address how organizations develop, monitor and ensure that internal security controls are active and functioning.
(CC5) Control Activities – These controls address how organizations establish security controls, connect controls to policies and procedures and assign duties.
(CC6) Logical and Physical Access Controls – These controls address how organizations manage physical security of devices as well as software and logical access restrictions to data.
(CC7) System Operations – These controls address how organizations handle system vulnerabilities, detect system operational issues and respond to security incidents.
(CC8) Change Management – These controls address how organizations handle development, testing, and deployment of new systems and applications.
(CC9) These controls define how organizations manage business risks, third parties, and external vendors as related to data security.
(A) Additional Criteria For Availability – These controls define additional standards for how organizations manage backups and overall system availability.
(C) Additional Criteria For Confidentiality – These controls address how confidential information is identified and protected from destruction.
(PI) Additional Criteria For Processing Integrity – These controls address how data is accurately processed and achieved.
(P) Additional Criteria For Privacy – These controls address how personal information is collected, retained and secured by the organizations.
Looking for the full set of SOC 2 controls and requirements? Download our SOC 2 Control List Excel
Preparing and Implement SOC 2 Controls
Implementing SOC 2 controls can appear overwhelming. Building a robust security program and preforming a SOC 2 readiness assessment can make your team better prepared to go through a security audit and achieve SOC 2 certification.
Learn how Dash ComplyOps can help your team prepare and achieve SOC 2 certification in the cloud.
- Utilize Dash to create custom administrative policies built around your organization and IT infrastructure.
- Enforce policy standards and SOC 2 security controls through Dash continuous compliance monitoring.
- Gather SOC 2 security evidence and create reports to simplify auditing and security evaluation
- Work with audit partner to complete a SOC 2 audit and achieve SOC 2 certification.